What is a stack or LIFO ?
LIFO, which stands for Last In, First Out, is a data organization method commonly used in digital design and computer science. The LIFO principle dictates that the most recently added item is the first one to be removed. This concept is analogous to a stack of plates, where the last plate placed on top is the first one to be taken off.

How does it work ?
LIFO is the fundamental principle behind the stack data structure:
- New elements are added to the top (push operation)
- Elements are removed from the top (pop operation)
- The most recently added element is always at the top
Where is a stack mostly used ?
LIFO is used in various aspects of memory management and program execution, but is most often used for function calls. When a function is called, its parameters and return address are pushed onto a stack. When the function returns, these values are popped off.
What are the advantages of LIFO ?
- Simple and efficient implementation
- Constant time complexity for push and pop operations (O(1))
- Well-suited for applications where recent data is more relevant
Verilog Stack Example
module lifo #(parameter WIDTH = 32, parameter DEPTH = 16)(
input wire clk,
input wire rst,
input wire push,
input wire pop,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] data_in,
output reg [WIDTH-1:0] data_out,
output reg empty,
output reg full
);
reg [WIDTH-1:0] stack [0:DEPTH-1];
reg [$clog2(DEPTH):0] stack_ptr;
always @(posedge clk or posedge rst) begin
if (rst) begin
stack_ptr <= 0;
empty <= 1;
full <= 0;
end else begin
if (push && !full) begin
stack[stack_ptr] <= data_in;
stack_ptr <= stack_ptr + 1;
empty <= 0;
if (stack_ptr == DEPTH - 1) begin
full <= 1;
end
end else if (pop && !empty) begin
stack_ptr <= stack_ptr - 1;
full <= 0;
if (stack_ptr == 1) begin
empty <= 1;
end
end
end
end
always @(*) begin
if (!empty & pop)
data_out = stack[stack_ptr - 1];
else
data_out = {WIDTH{1'b0}};
end
endmodule
Testbench
module lifo_tb;
// Parameters for the LIFO
parameter WIDTH = 16;
parameter DEPTH = 4; // Set a smaller depth for testing
// Testbench signals
reg clk;
reg rst;
reg push;
reg pop;
reg [WIDTH-1:0] data_in;
wire [WIDTH-1:0] data_out;
wire empty;
wire full;
// Instantiate the LIFO module
lifo #(
.WIDTH(WIDTH),
.DEPTH(DEPTH)
) uut (
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.push(push),
.pop(pop),
.data_in(data_in),
.data_out(data_out),
.empty(empty),
.full(full)
);
// Clock generation
initial begin
clk = 0;
forever #5 clk = ~clk; // 10 ns clock period
end
// Test sequence
initial begin
// Initialize signals
rst <= 1;
push <= 0;
pop <= 0;
data_in <= 0;
// Wait for a few clock cycles
#10;
// Release reset
rst <= 0;
for (integer i = 0; i < 20; i = i + 1) begin
@(posedge clk);
if ($random % 2) begin
push <= $random;
pop <= 0;
data_in <= $random;
end else begin
pop <= $random;
push <= 0;
end
$display("[%0t] Operation push=%0d pop=%0d data_in=0x%0h empty=%0b full=%0b", $time, push, pop, data_in, empty, full);
end
#100;
$finish;
end
endmodule
Simulation
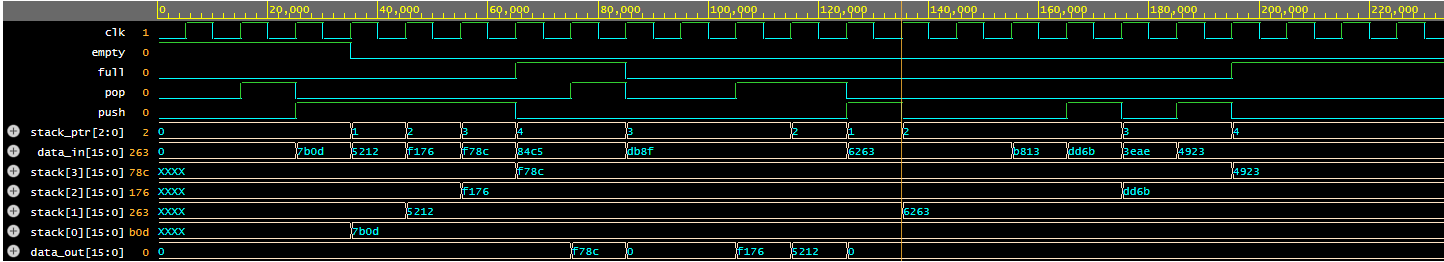
xcelium> run Pushing values onto the stack: [15000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x0 empty=1 full=0 [25000] Operation push=0 pop=1 data_in=0x0 empty=1 full=0 [35000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0x7b0d empty=1 full=0 [45000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0x5212 empty=0 full=0 [55000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0xf176 empty=0 full=0 [65000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0xf78c empty=0 full=0 [75000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x84c5 empty=0 full=1 [85000] Operation push=0 pop=1 data_in=0x84c5 empty=0 full=1 [95000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0xdb8f empty=0 full=0 [105000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0xdb8f empty=0 full=0 [115000] Operation push=0 pop=1 data_in=0xdb8f empty=0 full=0 [125000] Operation push=0 pop=1 data_in=0xdb8f empty=0 full=0 [135000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0x6263 empty=0 full=0 [145000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x6263 empty=0 full=0 [155000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x6263 empty=0 full=0 [165000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0xb813 empty=0 full=0 [175000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0xdd6b empty=0 full=0 [185000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x3eae empty=0 full=0 [195000] Operation push=1 pop=0 data_in=0x4923 empty=0 full=0 [205000] Operation push=0 pop=0 data_in=0x4923 empty=0 full=1 Simulation complete via $finish(1) at time 305 NS + 0
The push and pop signals are used to add and delete data from the stack. Any data that is added to a full stack will be lost.